Introduction to Mechanize with Python
Disclaimer: make sure to check the terms of use of the website you plan to interact with, a lot of websites forbids interaction from automation. Don’t do anything that could get you in trouble.
mechanize is a library to interact with websites. It fits in between high-level browser automation tools like Selenium and HTTP libraries like requests. It doesn’t handle Javascript, if that’s an issue for you, you should consider CasperJS. The big advantage of using mechanize compared to a higher level library is speed: it is an order of magnitude faster!
I use the following boilerplate code for all my programs with mechanize:
Set up user agent
Load cookies from a file
If the cookies are expired:
Go through the login flow
Interact with the website
Persist the cookies to a file
If you do the following instead:
Go through the login flow
Interact with the website
Then, you will end up going through the login flow as many times as you run the script. Not only will this be inefficient, but you would also take the risk of being blacklisted by the website’s owner for making too many requests. Let’s see in practice what this code looks like.
Boilerplate
Assuming that you want to log into a website and read a page that shows some JSON content, you would do something like this:
import os
import json
import cookielib
import mechanize
def getbrowser():
br = mechanize.Browser()
br.set_handle_redirect(True)
br.addheaders = [('User-agent', 'XXX')] # Set you user agent here
return br
def loadcookiejar():
cj = cookielib.LWPCookieJar()
if os.path.exists("cookies"):
cj.load("cookies")
return cj
def main():
br = getbrowser()
cj = loadcookiejar()
br.set_cookiejar(cj)
if len(cj) != 1:
url = 'https://XXX'
br.open(url)
# Select the first form
br.select_form(nr=0)
# Fill in some information
br["email"] = "XXXXXXX"
br["password"] = "YYYYYYY"
# Actually log in and set the cookies
br.submit()
# The page you are interested in
r = br.open("https://YYYY")
# Assumes that the content is JSON, otherwise use r.read()
print json.loads(r.read())
cj.save("cookies")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Now, some of you might wonder “how do you figure out what the URLS/parameter are for the stuff that you are interested in”. It is actually fairly easy to gather that information.
Figure out the API behind a website
This explanation assumes that you are using Google Chrome, tools exists with many other browser to do the same thing.
Open the Developer Console and go to the Network Tab. Click on the button to start a recording and navigate to a page.
You will see a bunch of requests, filter the kind that interests you, you generally want to see the requests for web pages and XHR, click on both and see if you find something interesting.
In my case, I am looking at a website that gives the location of my phone, I
filtered the XHR requests:
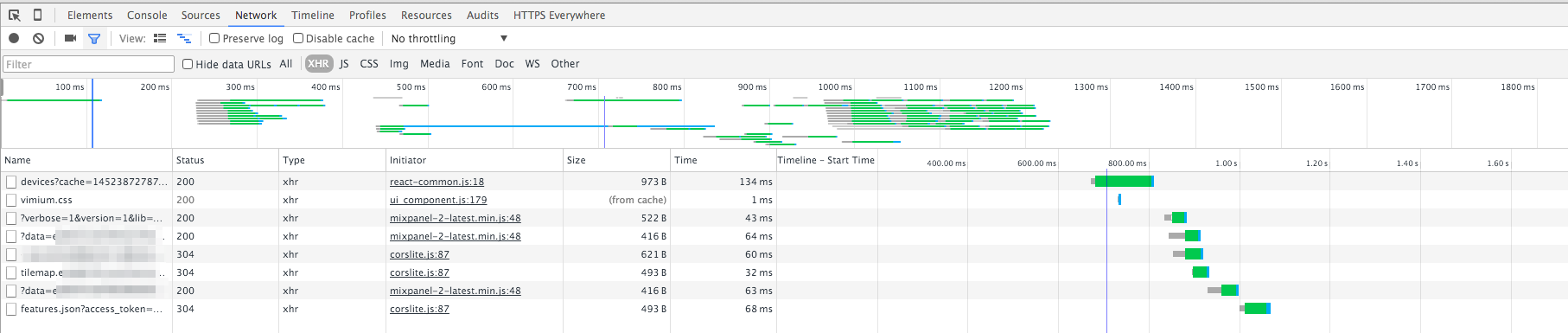
It looks like the first entry is very interesting:
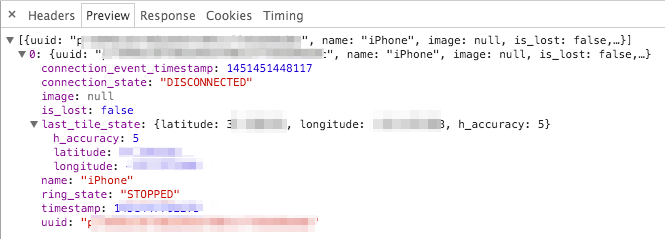
From there, right click on the request and you can copy the URL and information
to make the request from python or a terminal: